
My life was turned upside down when I was diagnosed with hypothyroidism. My thick, lustrous hair started falling out, revealing a painful realization of my hormonal imbalance. I was no longer the vibrant person I used to be. These symptoms were the initial signs of hypothyroidism.
The effects of hypothyroidism on my body were relentless. I felt constantly lethargic and unmotivated, and despite not eating much, I started gaining weight rapidly. My self-confidence plummeted, forcing me to withdraw from social activities and isolate myself from the world.
Determined to regain stability and balance in my life, I sought new treatments. My doctor prescribed a new thyroid medication and bioidentical hormonal therapy. I also discovered the importance of a nutritious diet and a low-impact exercise program.
What I Learned About Hypothyroidism Supplements
I learned about specific supplements that support thyroid health, including selenium, zinc, iodine, magnesium, and vitamin D3. These supplements addressed the nutrient deficiencies often linked to hypothyroidism and significantly improved my overall well-being. They became a cornerstone of my journey toward restoring both physical and mental health.
However, it is essential to take supplements under medical supervision, especially concerning IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1) levels, a hormone crucial for growth and metabolism. While IGF-1 is vital, consistently high levels can increase the risk of certain cancers and metabolic issues. Regular monitoring ensures these levels remain within a healthy range.
Additionally, prolonged use of supplements without breaks may lead to imbalances and side effects. Taking periodic breaks and undergoing regular assessments helps maintain optimal health. Consulting with a healthcare professional ensures the correct dosage and duration of supplementation, offering a safe and effective way to support thyroid health.
What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and depression. It affects millions of women worldwide, with women being about 10 times more likely than men to develop the condition.
Managing hypothyroidism is essential for overall health, and supplements can help improve symptoms, allowing women to regain control of their well-being.
Causes of Hypothyroidism in Women
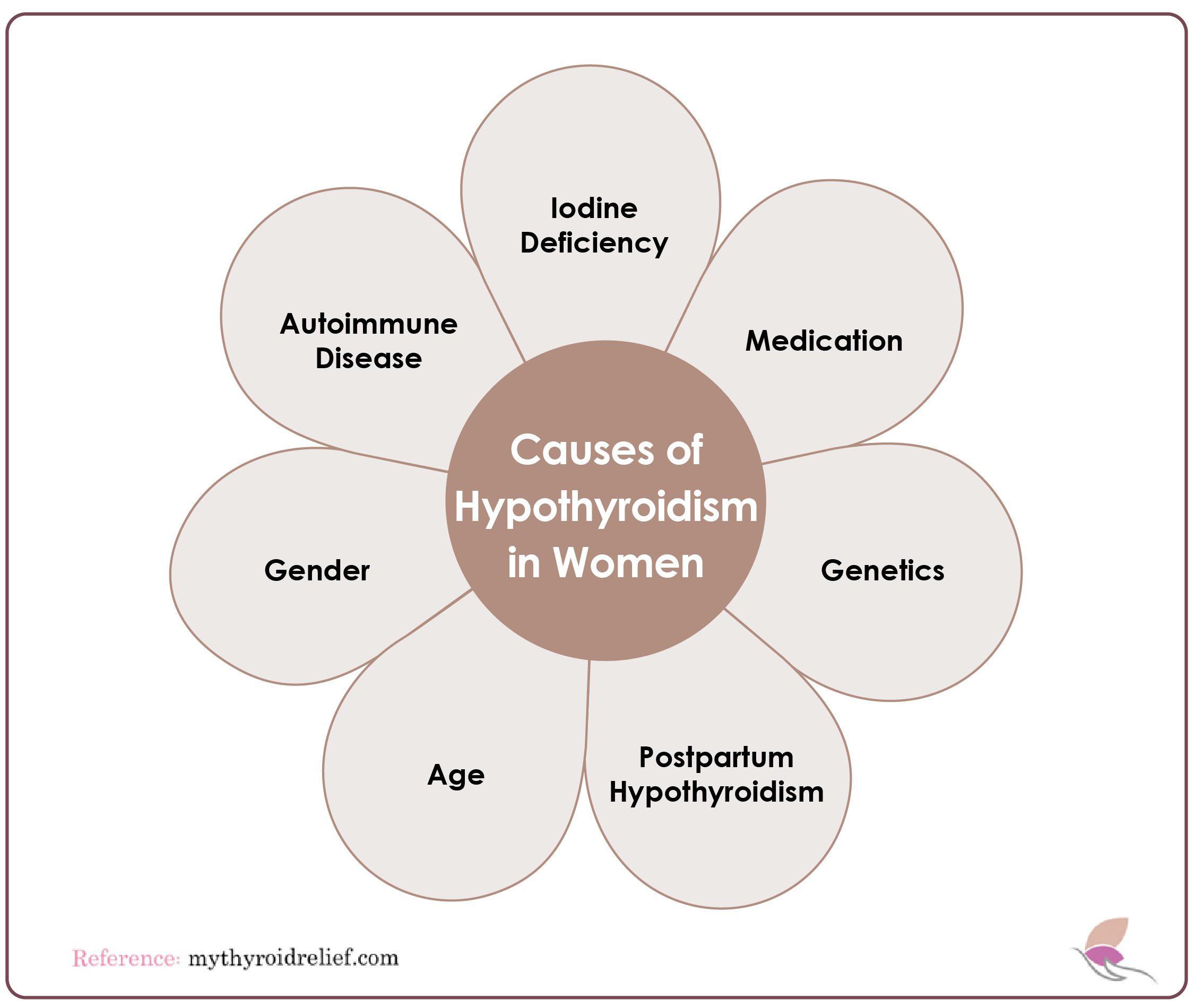
- Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. In hypothyroidism, the immune system may mistakenly attack the thyroid gland, preventing it from producing enough hormones.
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is an essential mineral required to produce thyroid hormones. If a woman’s diet doesn’t contain enough iodine, her thyroid gland may not produce enough hormones.
- Medication: Some medications can interfere with thyroid hormone medication, including medicines for seizures, antibiotics, and antidepressants. It is essential to discuss any medications you are taking with a doctor, as alternative treatments may be available.
- Age: Hypothyroidism is more common in women over the age of 60. The thyroid gland naturally becomes less active with age, making it harder to produce enough hormones. It’s more likely in women who’ve had children, as pregnancy can cause changes to the thyroid gland.
- Gender: Gender plays a role in hypothyroidism. Women are more likely to develop hypothyroidism than men, particularly as they age. This may be due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, or other life stages.
- Postpartum hypothyroidism: Postpartum thyroiditis is a condition that affects some women after giving birth. It is characterized by thyroid gland inflammation, which causes it to become underactive and produce fewer thyroid hormones. Postpartum hypothyroidism usually occurs within the first year after childbirth, with symptoms appearing between three and six months.
- Genetics: Several genes have been identified as potential contributors to hypothyroidism, including genes involved in the production of thyroid hormones and genes that affect the body’s ability to absorb iodine, a key component in the production of thyroid hormones. Studies suggest that some gene variations may increase the risk of autoimmune thyroid disease.
The Role of Supplements for Hypothyroidism
It’s important to understand that supplements can’t replace medical treatment for hypothyroidism. If you have hypothyroidism, you should always follow your doctor’s advice and take your prescribed medications. However, some supplements may be beneficial in helping to manage symptoms or even help to improve thyroid function.
1. Iodine

Iodine is essential for metabolism, hormone production, and brain and nervous system development. It is also critical for thyroid function, especially in women, as it is necessary for healthy thyroid hormone production. While various factors can contribute to hypothyroidism, iodine deficiency is one of the most common causes in women.
Some patients may require higher amounts of iodine due to problems with absorption from the food they consume, making supplementation more critical for them. Iodine is available in supplement form and food sources, providing an easy and affordable treatment for hypothyroidism. It can quickly replenish the body’s iodine stores, but it’s crucial to note that too much iodine can adversely affect health.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for iodine in adults is 150 mcg, and women with hypothyroidism should consult your doctor before starting supplementation. Additionally, iodine is best absorbed when taken alongside selenium, so women with hypothyroidism should consider supplements that contain both.
By replenishing iodine levels, women with hypothyroidism can support their thyroid health. However, talking to a healthcare provider before taking iodine supplements is important to ensure the proper dosage and prevent potential harm from excessive intake.
2. Selenium

3. Omega-3 fatty acids

Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their health benefits and may be necessary in treating hypothyroidism in women. They are found in various foods, such as fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, and are also available as supplements. These fatty acids are essential for proper body functioning, regulating hormones, and maintaining healthy cell membranes. Recent studies have found that omega-3 fatty acids may be especially beneficial for women with hypothyroidism.
One study found that supplementing with Omega-3 fatty acids for six months improved thyroid hormone levels, improving symptoms of hypothyroidism. Another study found that supplementing with Omega-3 fatty acids improved mood, memory, and concentration in women with hypothyroidism.
These studies suggest that this supplement may be effective for treating hypothyroidism in women. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to find the optimal dosage before taking it.
4. L-Tyrosine
This amino acid is found naturally in the body and is essential for producing the hormones T4 and T3. It supports thyroid function by helping the body synthesize these hormones. Low levels of L-tyrosine can lead to reduced hormone production, contributing to hypothyroid symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain.
In addition to its role in thyroid hormone production, L-tyrosine has been shown to improve mood and cognitive function. This is due to its ability to increase levels of dopamine and norepinephrine, neurotransmitters that regulate mood and mental clarity. This supplement can help alleviate some of the cognitive and emotional difficulties often experienced by individuals with hypothyroidism, especially women.
5. Vitamin B12

B12 plays an essential role in the body’s metabolism. It helps break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats and is also necessary for producing red blood cells. In addition, it is involved in the production of thyroid hormones. When levels of Vitamin B12 are low, it can decrease the production of thyroid hormones, resulting in symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Studies have shown that this supplement can help improve the symptoms of hypothyroidism in women. In a recent study, women with hypothyroidism who took daily Vitamin B12 experienced a significant reduction in their symptoms. They also experienced an increase in energy levels and an improvement in mood and concentration.
This supplement can be found in various foods, including beef liver, salmon, tuna, fortified cereals, and bread. However, women with hypothyroidism may need to take a supplement to get enough of the vitamin. The most stable form of Vitamin B12 is Cyanocobalamin. They are available in tablet, capsule, and liquid form and can be purchased without a prescription.
6. Zinc

This mineral is fundamental to the production of thyroid hormones and immune function. It supports the conversion of T4 to the active thyroid hormone T3, which is vital for proper thyroid function. Zinc supplementation can be particularly beneficial for individuals with hypothyroidism, especially if dietary intake is insufficient. Foods like oysters, red meat, poultry, and beans are excellent sources of zinc.
Recent studies have demonstrated that zinc can help improve thyroid hormone levels in individuals with hypothyroidism and alleviate common symptoms like fatigue, depression, and hair loss. Since zinc is necessary for metabolizing carbohydrates and amino acids, it supports overall thyroid health. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure the appropriate dosage, especially if you’re already managing thyroid conditions.
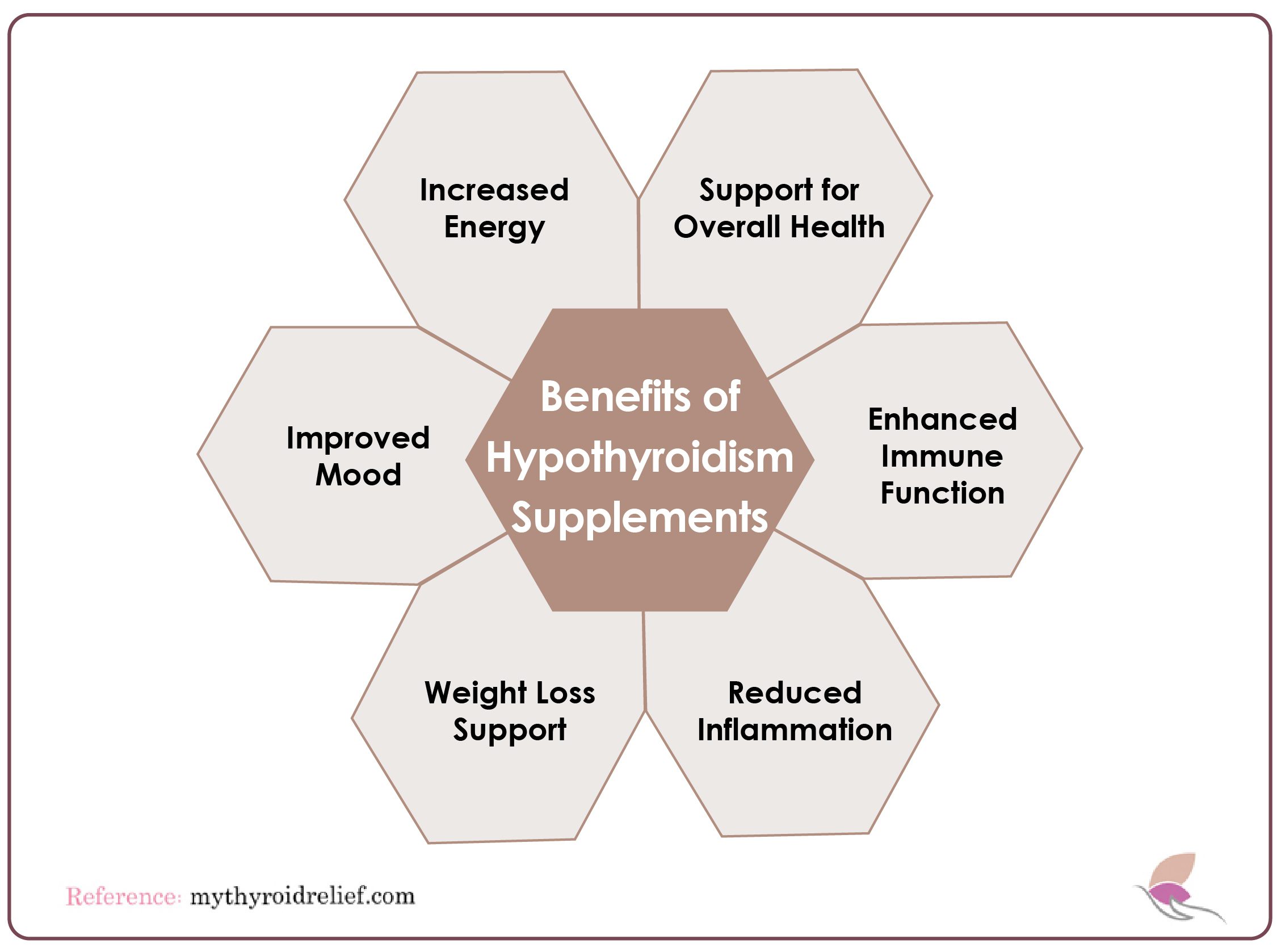
Benefits of Taking Hypothyroidism Supplements
Living with hypothyroidism can be a challenging experience. It can cause a range of unpleasant symptoms like fatigue, depression, and weight gain and can make it difficult for you to do the things you enjoy. Fortunately, many natural supplements can help you manage your hypothyroidism, and here are some of the benefits they can provide.
1. Increased Energy
One of the most common problems with hypothyroidism is fatigue, and taking certain supplements can help boost your energy levels. For example, tyrosine is an amino acid that can help increase your energy levels, while iodine is an important mineral for thyroid health. Both of these are available in supplement form and can help you feel more energized and alert.
2. Improved Mood
Hypothyroidism can also cause depression and mood swings, which can make it difficult to enjoy activities and socialize with others. Taking supplements like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B12 can improve your mood and help you get through the day.
3. Weight Loss
Many people with hypothyroidism struggle with weight gain, and this can be especially true if you’re not getting enough of the essential vitamins and minerals your body needs. Taking supplements like selenium, zinc, and vitamin D-3, which is the most absorbable form of vitamin D, can help boost your metabolism and make it easier to shed extra pounds.
4. Reduced Inflammation
Hypothyroidism can cause inflammation in the body, which can lead to joint pain, headaches, and other uncomfortable symptoms. Taking supplements like turmeric and ginger can help reduce inflammation, making it easier to move and be active.
5. Enhancing immune function
Hypothyroidism can weaken the immune system, leaving individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Supplements such as vitamin C, zinc, and probiotics, liposomal glutathione, alpha lipoic acid can help support immune function glucose control and reduce the risk of infections.
6. Supporting overall health
Many of the supplements that are beneficial for hypothyroidism also have general health benefits. For example, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory effects and can help reduce the risk of heart disease and arthritis. If you have hypothyroidism, you might be looking for the right supplement to help manage your condition. But with so many options on the market, knowing which one is best for you can be difficult. The first step in selecting a supplement is to talk to your doctor.
How to Choose the Best Form for Each Hypothyroidism Supplement
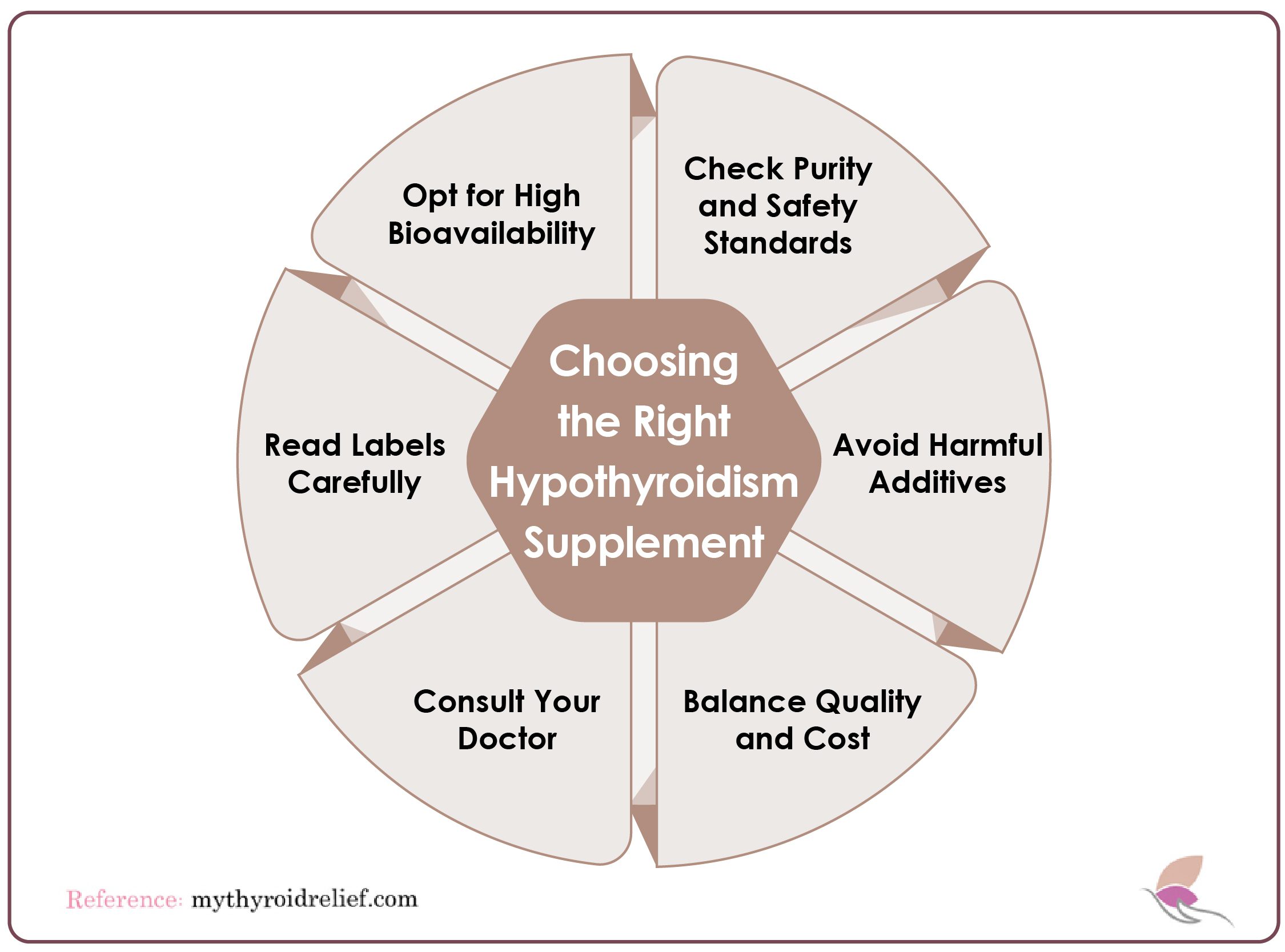
Different forms of supplements may have varying bioavailability or absorption rates.
- Check for purity and safety: If you are taking fish oil supplements for omega-3s, look for products sourced from wild fish and purified to remove contaminants like heavy metals and PCBs.
- Avoid harmful additives and fillers: Check the ingredients list on supplements and avoid products that contain unnecessary fillers, additives, or artificial colors and flavors.
- Read the label carefully: Only take a supplement containing ingredients proven safe and effective for treating hypothyroidism.
- Opt for Quality and Affordability: Look for reputable supplements with quality ingredients, and make the most of discounts or sales to stay within your budget without compromising on quality.
- Talk to your doctor: They can advise which type is most appropriate for you and your condition. Also, your doctor helps you determine the right dosage. Your doctor may also recommend a combination of supplements, so getting their input is essential before making any decisions. After speaking with your doctor, thinking carefully about the supplement’s components is crucial.
- Read the label carefully: Only take a supplement containing ingredients proven safe and effective for treating hypothyroidism.
Additional Supplements for Women with Hypothyroidism
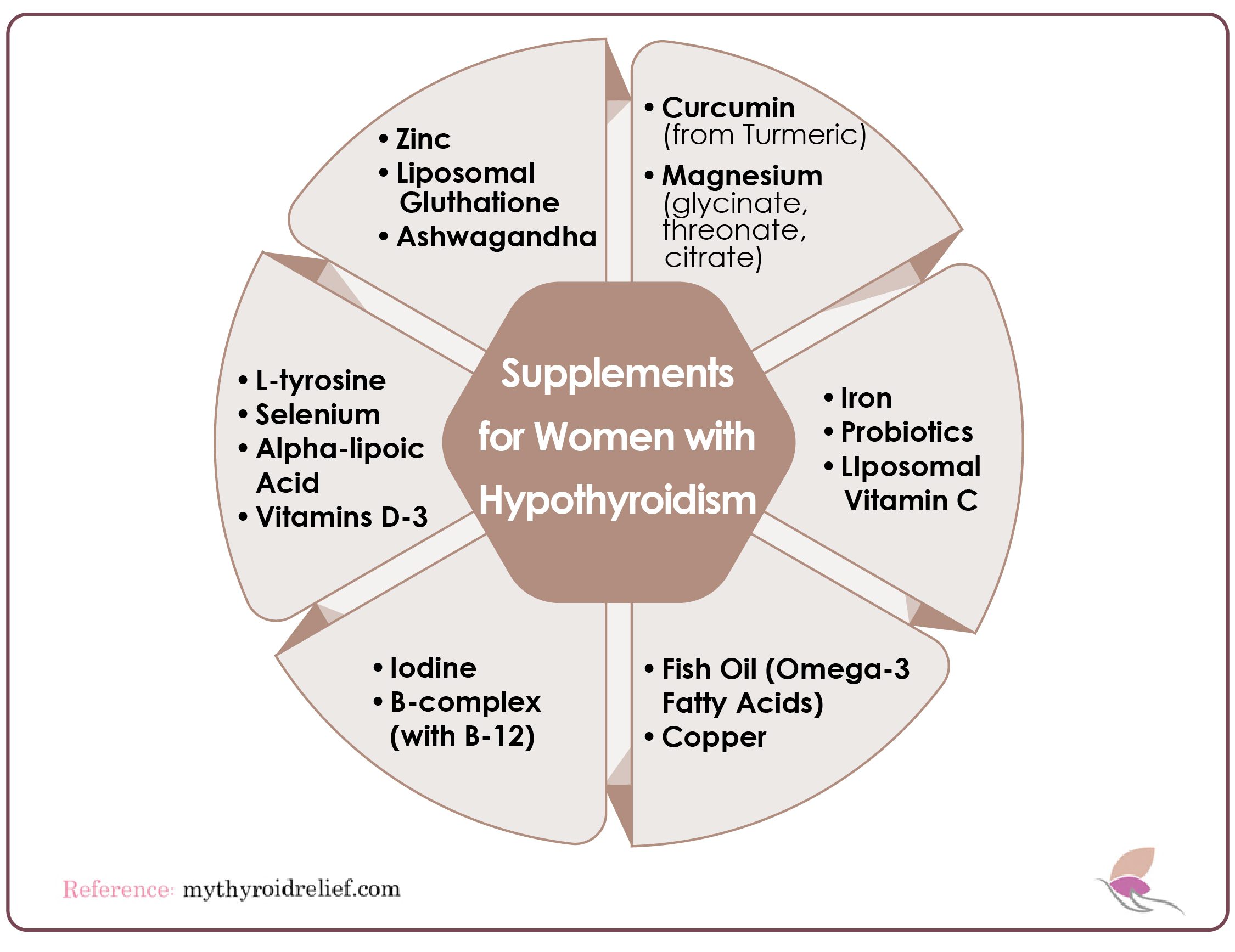
The body relies on iron to produce hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood. It also supports the synthesis and metabolism of thyroid hormones. Iron deficiency is common in hypothyroidism and can worsen fatigue. Include iron-rich foods like red meat, spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals in your diet. If taking supplements, pair them with vitamin C for improved absorption.
Conclusion
Supplements can be beneficial for managing hypothyroidism, but they should accompany other treatments, such as medication, diet, and lifestyle changes. To ensure safety and effectiveness, it’s important to select high-quality supplements from reliable sources, follow the recommended dosages, and have regular blood tests to monitor thyroid function.
A balanced organic diet rich in nutrient-dense foods like iodine, selenium, magnesium, zinc, and omega-3s supports thyroid function. Lifestyle habits like stress management, exercise, and adequate sleep can improve overall health and thyroid function. Supplementation is one part of a comprehensive plan for managing hypothyroidism; work with a healthcare team for informed decisions.
References
- American Thyroid Association. (2020). Hypothyroidism. https://www.thyroid.org/hypothyroidism/
- Elizabeth S.B (2019) https://www.everydayhealth.com/hs/healthy-living-with-hypothyroidism/vitamins/
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Hypothyroidism. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypothyroidism/symptoms-causes/syc-20350284
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2020). Hypothyroidism. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypothyroidism/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352967
- National Institutes of Health. (2020). Hypothyroidism. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/hypothyroidism
Thanks for shedding light on ‘Hypothyroidism Supplements for Women.’ It’s an important topic that many of us need to navigate. While supplements can be beneficial, it’s crucial to remember they’re not a substitute for prescribed medication. Consulting a healthcare professional is vital to finding the correct dose and determining if they are beneficial for our case. Remember to take breaks and undergo regular testing to monitor nutrient levels and avoid potential health risks. Keep up the informative posts!
Thank you so much for sharing your personal journey with hypothyroidism. I truly resonated with your experience, especially the struggle with hair loss, fatigue, and unexpected weight gain. It’s so encouraging to hear how proactive you’ve been in finding not only the right medication but also incorporating lifestyle changes and supplements to support your recovery.