
The primary treatment for hypothyroidism is thyroid hormone replacement therapy, such as levothyroxine, an exogenous form of T4. This medication helps restore normal thyroid hormone levels, alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. However, managing hypothyroidism isn’t limited to medication alone. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and specific nutritional supplements can help support thyroid function and overall health.
Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels by a healthcare professional is crucial to ensure that treatment remains effective. Also, incorporating dietary supplements and making lifestyle changes can significantly support thyroid health and improve symptoms.
Supplements for hypothyroidism
Iodine
Iodine plays a crucial role in thyroid hormone production. It occurs naturally in foods like seaweed, grains, dairy products, and eggs. However, its distribution is uneven worldwide. Some regions are rich in iodine, while others have deficient levels. To combat iodine deficiency, many countries have implemented iodine supplementation programs, such as adding iodine to salt (known as salt iodization).
Several factors can interfere with iodine absorption. People with intestinal malabsorption, those who have undergone bariatric surgery, or individuals consuming large amounts of goitrogen-rich foods may face absorption issues. Goitrogens are found in foods like soy, flaxseeds, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and cabbage. These foods counteract iodine absorption and, when consumed in excess, can worsen iodine deficiency or hypothyroidism, especially in individuals already at risk.
Although low iodine levels can lead to hypothyroidism by affecting thyroid hormone production, excessive iodine intake can also disrupt thyroid function. Too much iodine can suppress thyroid activity, particularly in people with autoimmune thyroid conditions, making them more sensitive to iodine’s inhibitory effects. The exact mechanism behind this reaction is still unknown, but research shows that iodine has an auto-regulatory inhibitory effect on the thyroid gland.
Therefore, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider to determine the right iodine supplementation dose and test thyroid function before taking iodine supplements. The recommended daily dose of iodine for most adults is 150 micrograms. However, some individuals may require higher doses to maintain adequate iodine levels.
Selenium
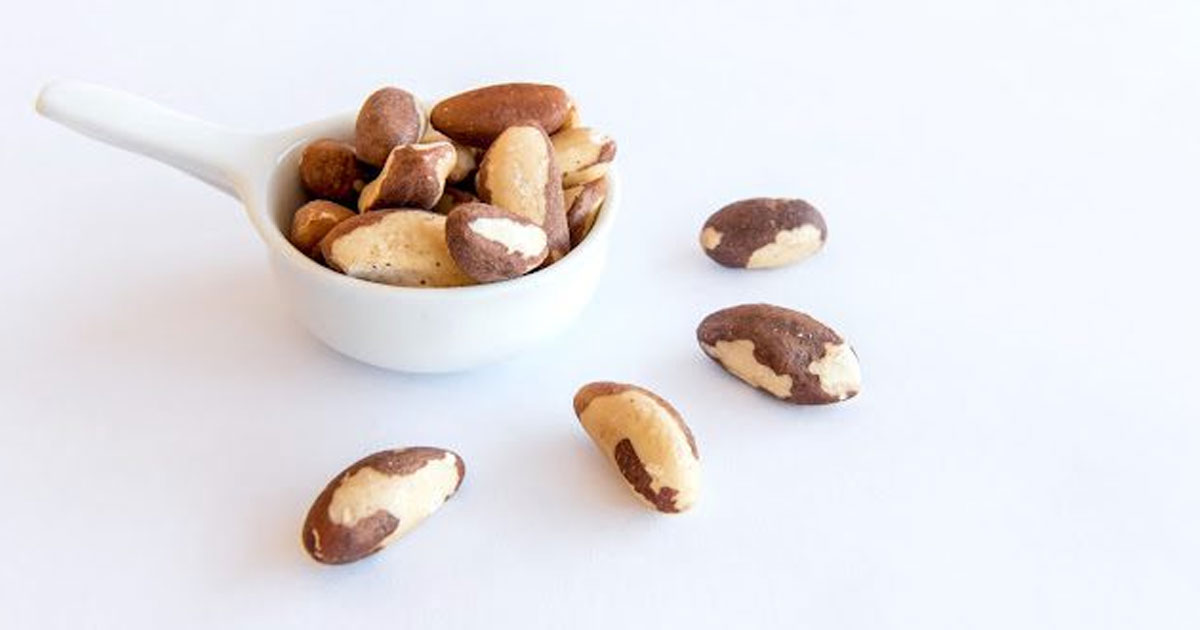

Selenium plays a critical role in thyroid hormone metabolism by helping convert T4 (the inactive form) into T3 (the active form). It also protects the thyroid from oxidative damage caused by free radicals and may help reduce thyroid antibodies in people with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Brazil nuts are one of the richest natural sources of selenium, but they can also be found in seafood, organ meats, and grains. Inadequate selenium levels are associated with an increased risk of thyroid problems, especially in people already prone to autoimmune thyroid disease. However, over-supplementing with selenium can be toxic, so it’s best to stick to the recommended dose.
Zinc
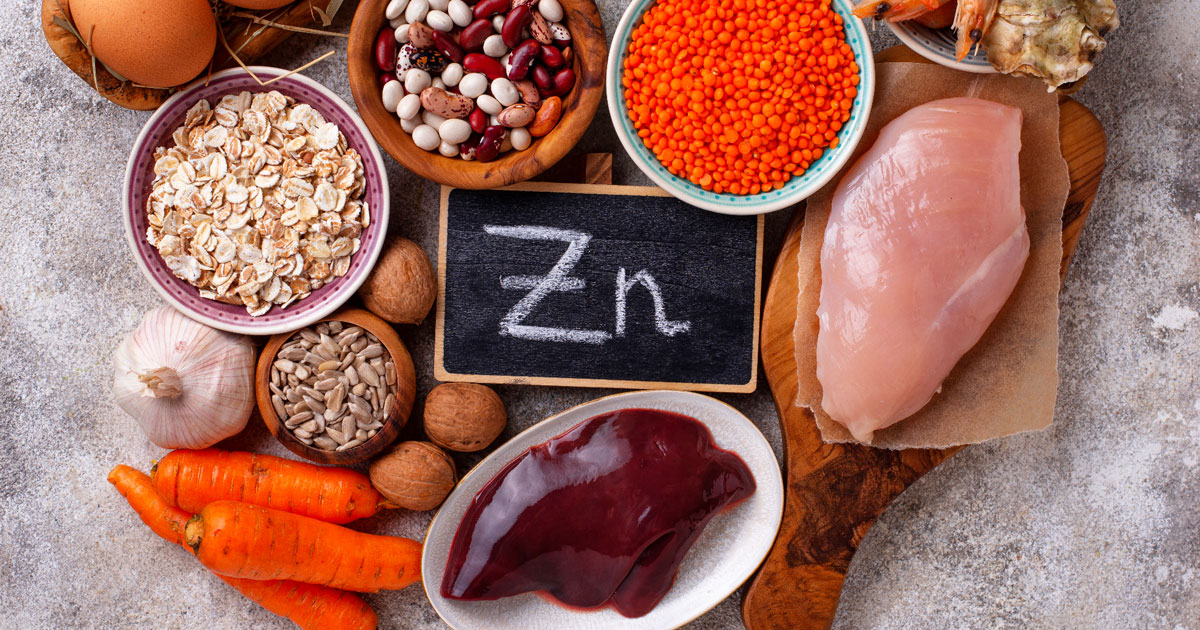

This supplement is essential for the synthesis of thyroid hormones and plays a key role in the body’s immune response. A zinc deficiency can impair the thyroid’s ability to produce hormones, leading to worsened hypothyroid symptoms. Common sources of zinc include shellfish, beef, poultry, and whole grains. Zinc also enhances the body’s ability to absorb thyroid hormones, which can improve the effectiveness of thyroid medication in individuals with hypothyroidism. For those who have thyroid-related issues, a deficiency in zinc can slow the recovery process, making it an important supplement to consider.
Vitamin A
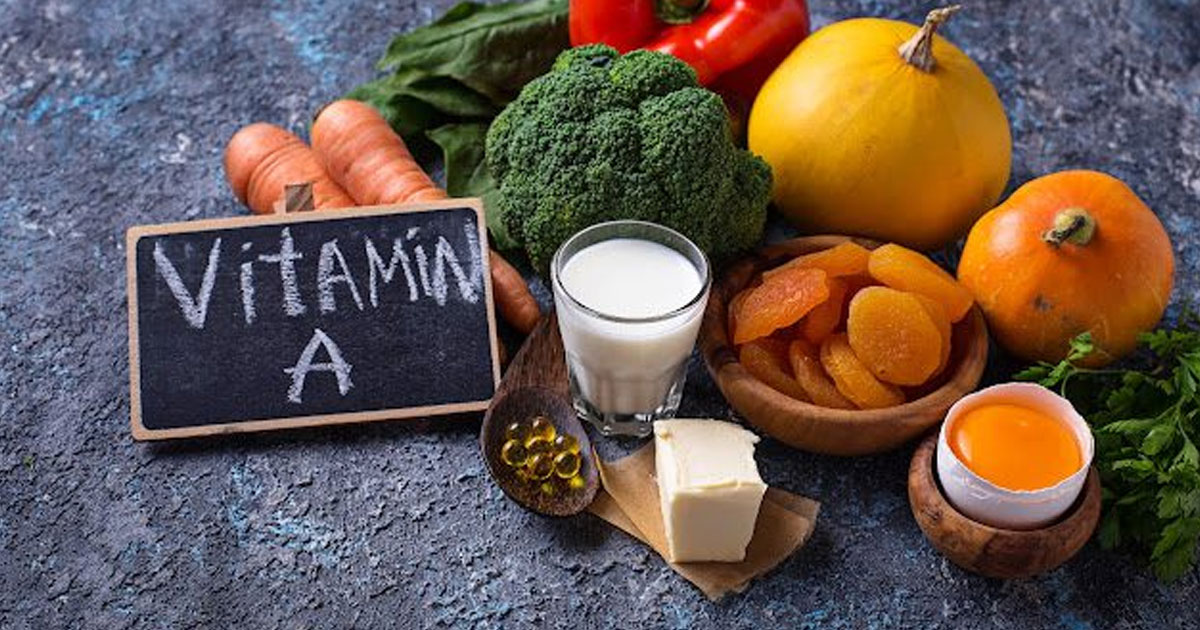

This supplement supports the proper functioning of the thyroid gland by regulating the production of thyroid hormones. A deficiency in vitamin A can impair thyroid function, and hypothyroidism itself can reduce the body’s ability to convert beta-carotene into the active form of vitamin A, leading to a deficiency. Additionally, vitamin A plays an important role in vision, immune health, and reproduction. Including foods rich in vitamin A, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, liver, and fish oil, can be beneficial for maintaining healthy thyroid function. Sources include Green leafy vegetables, liver, milk, fish oil, and eggs.
Iron
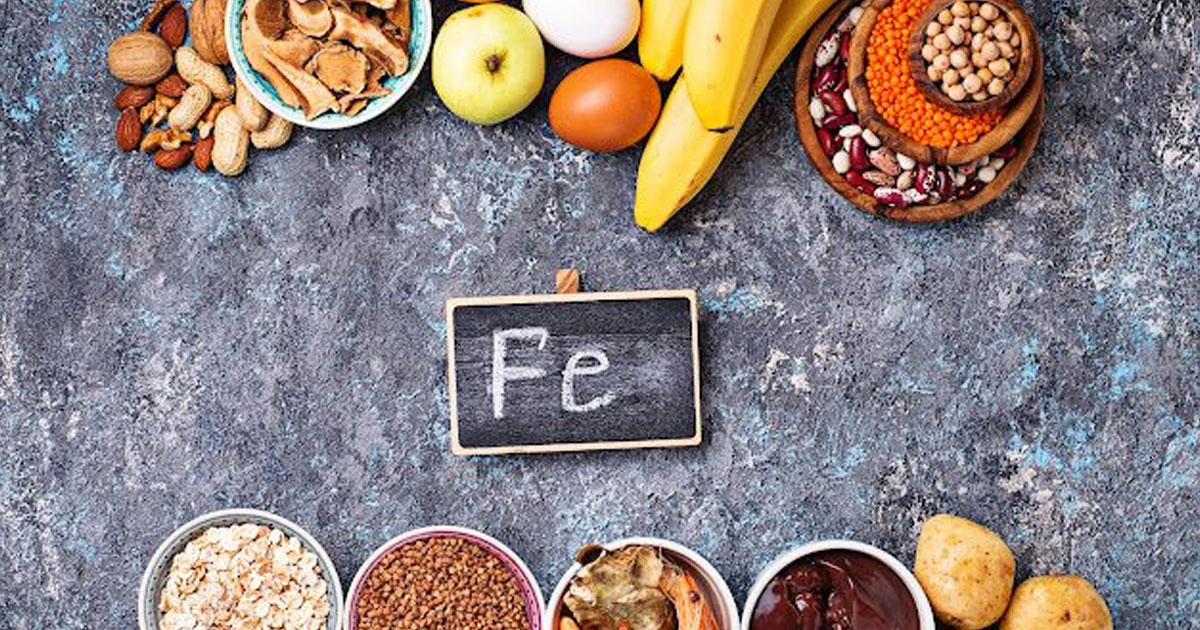

Iron is crucial for thyroid hormone production and for the conversion of T4 to T3. A lack of iron can lead to anemia, which further worsens hypothyroid symptoms, such as fatigue and poor concentration. People with hypothyroidism are more susceptible to iron deficiency due to impaired absorption. Good sources of iron include red meat, liver, beans, lentils, and dark leafy greens. If you are found to have low iron levels, taking an iron supplement under medical supervision can help improve thyroid function and overall energy levels. Sources include Liver, red meat, beans, and nuts.
Vitamin B

The B vitamins, particularly B12, are essential for energy production, nerve function, and red blood cell formation. People with hypothyroidism, especially those with Hashimoto’s disease, often have low levels of B12, which can contribute to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and memory problems. Supplementing with a full B-complex can provide holistic support for thyroid health, as it ensures a balanced intake of all the B vitamins. Fish, eggs, whole grains, and leafy greens are excellent sources of B vitamins.
Vitamin D

Vitamin D is critical for immune function and bone health, and many hypothyroid patients suffer from low levels of this nutrient. Deficiency in vitamin D has been linked to an increased risk of autoimmune diseases, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Supplementing with vitamin D3 can help regulate the immune system and improve overall thyroid function. In addition to taking supplements, exposure to sunlight and consuming vitamin D-rich foods such as fatty fish, fish liver oil, and fortified foods can help maintain adequate levels. The recommended Daily Dose: is 600–800 IU, though higher doses may be needed for those with deficiencies.
Vitamin E

This supplement is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the thyroid gland from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. This vitamin is especially beneficial when taken alongside thyroid hormone replacement therapy, such as levothyroxine, as it can enhance the medication’s effectiveness and provide additional protection for the thyroid gland. Food sources of vitamin E include plant oils, nuts, and cereals. Incorporating these foods or taking supplements can support overall thyroid health. Recommended Daily Dose is 15 mg for adults.
Omega-3 fatty acids

Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is a common issue in individuals with autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s disease, which can further impair thyroid function. Omega-3 supplements can help reduce inflammation, promote heart health, and support the thyroid gland’s overall function. Including omega-3-rich foods in your diet or using high-quality supplements can be a beneficial part of managing hypothyroidism. Recommended Daily Dose is 250–500 mg of EPA and DHA combined.
How to Detect Nutrient Deficiencies
Detecting nutrient deficiencies is crucial for anyone dealing with hypothyroidism or other thyroid-related conditions. Nutrient deficiencies can exacerbate symptoms of thyroid disorders and impede effective treatment. To determine if you have a deficiency, the most reliable method is to conduct blood tests. There are two main types of tests you can choose from: venous blood tests and finger-prick blood tests.
A venous blood test is conducted by a healthcare professional and involves drawing blood from a vein, typically in the arm. This method allows for a comprehensive analysis of various nutrients such as iodine, selenium, iron, vitamin D, and B vitamins, all of which play essential roles in thyroid function. The results from a venous blood test are highly accurate, making it a preferred option for many patients. It provides a detailed picture of your health, enabling your healthcare provider to make informed recommendations for managing your condition.
Alternatively, a finger-prick blood test is a convenient home-based option. With a simple prick of the finger, you can collect a small sample of blood and send it to a lab for analysis. While finger-prick tests are less comprehensive than venous tests, they still provide valuable insights into key nutrient levels. Moreover, this method is especially useful for those who may have limited access to healthcare facilities or prefer the convenience of home testing. However, it is recommended to follow up with your healthcare provider for a more thorough assessment if deficiencies are detected.
Addressing nutrient deficiencies is essential for optimizing thyroid function and managing hypothyroidism effectively. By incorporating foods rich in necessary vitamins and minerals or by taking supplements as recommended by your doctor, you can support your thyroid and overall health. Regular blood tests can help monitor your nutrient levels, identify any imbalances, and prevent the worsening of hypothyroid symptoms.
How Long Does it Take for Supplements to Work?
When managing thyroid health, many people wonder how long it will take for supplements to show their effects. The time frame for noticeable changes varies depending on several factors, such as the severity of the nutrient deficiency, the type of supplement used, and the individual’s overall health. For those with mild deficiencies, some supplements may begin to show improvements in just a few days to a couple of weeks. However, it is not uncommon for it to take several months to fully restore optimal nutrient levels and achieve desired health outcomes.
One of the key factors influencing the effectiveness of supplements is the level of deficiency. For example, someone with a severe vitamin D deficiency may need to take higher doses and wait longer to notice improvements compared to someone with a milder deficiency. The form of the supplement also plays a role. Liquid supplements are generally absorbed more quickly than capsules or tablets. Pairing certain nutrients together, such as vitamin D with magnesium or calcium, can also enhance absorption and speed up the effects of supplementation.
Digestive health is another critical factor that can impact how quickly supplements work. If a person has digestive issues like leaky gut syndrome or malabsorption, they may not fully benefit from oral supplements. In such cases, addressing digestive health first may be necessary to optimize nutrient absorption. Overall lifestyle and dietary habits can also play a role; individuals who follow a balanced diet and maintain a healthy lifestyle may experience quicker and more noticeable improvements when taking supplements.
Monitoring nutrient levels through regular blood tests is crucial while taking supplements. This helps ensure that you are receiving the appropriate dosage and allows your healthcare provider to make any necessary adjustments. Being patient and consistent with supplementation, along with regular follow-ups, can ultimately lead to better thyroid health and symptom management.
Tips and Precautions
Taking supplements can be a beneficial strategy for managing thyroid health, but it’s important to follow specific guidelines to maximize their effectiveness and avoid potential complications. One of the most important steps is to consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen. Your doctor can recommend the appropriate supplements based on your specific deficiencies and health status, ensuring that you are not taking unnecessary or potentially harmful supplements. This is particularly crucial for individuals with thyroid disorders, as some supplements can interfere with thyroid hormone absorption or interact with other medications.
When taking supplements alongside thyroid medication, timing is essential. Certain supplements, such as calcium and iron, can inhibit the absorption of thyroid medication, reducing its effectiveness. To avoid this issue, take supplements at least four hours apart from your thyroid medication. This precaution ensures proper absorption of your medication and maintains its intended efficacy. While iodine is necessary for thyroid hormone production, too much can aggravate thyroid conditions, particularly autoimmune thyroid diseases.
Choosing high-quality supplements is another important consideration. Opt for brands that undergo third-party testing to verify their purity and potency. Quality supplements are less likely to contain contaminants and provide a more consistent dosage, which is important for managing nutrient deficiencies effectively. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is also key to supporting thyroid health.
A balanced diet rich in nutrients, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption can all contribute to better thyroid function. Stress management through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can also be beneficial, as high-stress levels can negatively impact thyroid health. By following these tips and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can safely incorporate supplements into your thyroid management plan and improve your overall health.
References
- https://www.everydayhealth.com/hs/healthy-living-with-hypothyroidism/vitamins/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/thyroid-vitamins
- https://www.womenshealthnetwork.com/thyroid-health/natural-supplements-multivitamins-for-hypothyroidism/
- https://coopercomplete.com/blog/supplements-for-thyroid-health/
Thanks in support of sharing such a pleasant idea, article is nice,
thats why i have read it fully
Thanks for your support. I have more articles about thyroid and some recipes that can be helpful to you.
Fantastic post! I thoroughly enjoyed reading it, and the insights on how to detect nutrient deficiency were particularly enlightening. The information provided has added significantly to my knowledge on the subject. Thank you for sharing such valuable content!
This is such an informative post. I will visit your blog more often. Thanks for sharing this useful information.
Hi Jessica,
Thank you so much! I’m thrilled you found the post informative and plan to visit my blog more often. It’s always a pleasure to share useful information with readers like you. Please let me know if you have any specific topics you’d like to see covered in future posts!