What is Dental Health?
Dental health, also known as oral health, involves caring for the mouth, teeth, gums, and tongue. It plays a crucial role in overall well-being, particularly for individuals with thyroid disorders. Establishing good dental hygiene habits early in life can significantly reduce the risk of cavities, tooth decay, and other oral issues. Teaching children proper oral care from a young age helps instill habits that last a lifetime.
For people with thyroid conditions, maintaining oral health is even more critical. Poor dental hygiene can lead to systemic inflammation, which may affect thyroid function. Additionally, certain dental treatments especially those involving heavy metals can pose risks to thyroid health. Being aware of these concerns and discussing them with a dentist helps thyroid patients make informed decisions about their oral care.
How Dental Health Affects General Well-being
Dental health is closely linked to overall health and plays a critical role in the proper functioning of various bodily systems. Poor oral hygiene can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria, which may enter the bloodstream and affect other organs, resulting in systemic health problems. Neglecting oral care can also lead to conditions like gingivitis and periodontal disease, both of which are linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Key Connections Between Oral and General Health
1. Bacterial Infections
When dental hygiene is poor, bacteria can accumulate in the mouth, leading to infections. These bacteria may enter the bloodstream through the gums, triggering inflammation that contributes to conditions like endocarditis, an infection of the heart lining.
2. Chronic Inflammation
Persistent oral infections can cause chronic inflammation, which plays a role in many health issues, including autoimmune diseases and chronic pain conditions. Inflammation that begins in the mouth can also worsen systemic inflammation, complicating pre-existing health problems.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
Tooth decay and gum disease can make it difficult to chew and swallow, potentially impacting your diet. This can lead to nutritional deficiencies that affect your energy levels and overall well-being.
4. Mental Health
Poor dental health can significantly impact mental health. It can lower self-esteem and contribute to social anxiety, leading to social withdrawal and a reduced quality of life.
5. Link to Systemic Diseases
Research shows a strong connection between poor oral health and systemic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues. Maintaining good dental hygiene is key to reducing the risk of developing these serious health problems.
Common Dental Health Issues Associated with Thyroid Disorders
Individuals with thyroid disorders often face a variety of oral health challenges that can significantly impact their quality of life. Understanding these common dental problems is crucial for effectively managing both thyroid health and oral hygiene.
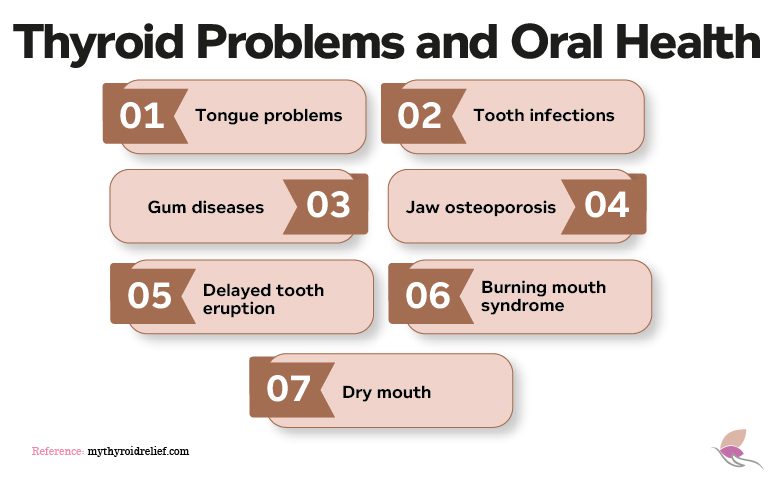
1. Tongue Problems
A scalloped tongue can indicate various health conditions, including low thyroid hormone levels. Research shows that hypothyroidism causes the thyroid gland to shrink and change shape, resulting in a scalloped tongue.
Because the thyroid gland is closely linked to the digestive system, individuals with scalloped tongues often experience difficulty swallowing, chewing food, and even talking.
Hypothyroidism is a major cause of tongue enlargement (macroglossia) in children, particularly those with Hashimoto’s disease. This condition can lead to speech difficulties, drooling, and problems with eating, chewing, and swallowing. Children with hypothyroidism may also experience sleep difficulties, snoring, and high-pitched breathing.
Taste disorders (dysgeusia) are common in patients with primary hypothyroidism. These disorders can lead to anorexia and loss of appetite, often observed in hypothyroidism patients.
2. Tooth Infections
Individuals with hypothyroidism are more prone to tooth infections, which result from dental cavities, gum disease, tooth sensitivity, and decaying teeth. Low thyroid hormone levels hinder the body’s ability to fight infections, resulting in a slower healing process.
3. Gum Diseases
Patients with thyroid disorders are at higher risk of developing gum disease. Those with hypothyroidism, in particular, may experience excessive gum bleeding, which increases the risk of infections and conditions such as periodontitis, gingivitis, gum inflammation, and, in extreme cases, bad breath and blood clot formation.
4. Jaw Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become fragile, increasing the risk of fractures. Contributing factors include inadequate nutrition, hyperthyroidism, and other underlying medical conditions.
Jaw osteoporosis can also be an indication of hypothyroidism. A complication of hyperthyroidism is rapid bone loss due to elevated blood levels of thyroid hormones. These hormones play a role in the rate of bone replacement. For patients with hyperthyroidism, the rate at which osteoblasts replace bone cannot keep up with the rate of bone loss, resulting in osteoporosis over time.
5. Delayed Tooth Eruption
Delayed tooth eruption can be caused by various factors, primarily related to a child’s diet and nutrition. Deficiencies in key nutrients, particularly calcium and vitamin D, can delay tooth eruption. However, it is also a significant indicator of hypothyroidism.
6. Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is characterized by a burning sensation in the tongue, lips, and sometimes the entire mouth. While there is no definitive medical cause for this syndrome, it is associated with thyroid disorders, particularly in women during menopause.
The incidence of BMS is higher in patients with hyperthyroidism than in those with hypothyroidism. Studies show that treatment for thyroid diseases can significantly improve symptoms of BMS.
7. Dry Mouth
Dry mouth is a common symptom in patients with thyroid disorders, often resulting from decreased salivary gland output. It can also be a side effect of thyroid-related conditions, such as Sjögren’s syndrome, an autoimmune disorder.
This symptom is more commonly observed in hyperthyroidism patients than in those with hypothyroidism. Individuals with dry mouth are at a higher risk of tooth decay.
8. Delayed Wound Healing
Thyroid hormone imbalances can affect various body functions, including the healing process and the body’s ability to fight infections.
What is the Relationship Between Dental Health and the Thyroid?
The connection between dental health and the thyroid is a significant one, forming a two-way relationship where each can influence the other. Poor oral health can disrupt thyroid function, while thyroid health can also affect oral health. Understanding this relationship is essential for maintaining overall wellness, especially for individuals with thyroid conditions.
1. How Dental Health Affects the Thyroid
A. Autoimmune Triggers
Research suggests that oral health issues may contribute to the development of autoimmune thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. Harmful bacteria from conditions like gum disease can enter the bloodstream, affecting gut health—a critical factor in immune system regulation. This disruption can trigger an overactive immune response, exacerbating thyroid-related conditions. For instance, bacteria from periodontal disease can cause systemic inflammation, influencing autoimmune responses that target the thyroid gland.
B. Dental Materials
Certain dental materials, including mercury fillings, specific inlays, or implants, may provoke autoimmune reactions in sensitive individuals. These reactions often arise from incompatibility between the body’s biochemistry and the materials used in treatments. For instance, patients with mercury sensitivity have reported improved symptoms after switching to mercury-free or biocompatible materials like composite resin.
2. How Thyroid Disorders Impact Dental Health
A. Increased Risk of Infections
Individuals with thyroid disorders, particularly hypothyroidism, often experience a weakened immune system, making them more susceptible to oral infections. This vulnerability can lead to gum disease, tooth decay, and slower healing after dental procedures. For example, hypothyroid patients undergoing tooth extractions may face extended recovery periods due to reduced metabolic rates and impaired healing responses.
B. Chronic inflammation in the gums
Thyroid dysfunction can increase the risk of periodontal conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis. These inflammatory diseases can worsen if left untreated, creating a cycle of systemic inflammation that further impacts thyroid health. Inflammation in the gums can elevate systemic inflammatory markers, potentially aggravating autoimmune thyroid conditions.
The Effect of Poor Oral Hygiene on Thyroid and Dental Health
Poor oral hygiene can indirectly impact thyroid function, particularly in individuals with pre-existing thyroid disorders. While no direct causal link exists between oral hygiene and thyroid dysfunction, several factors underscore the importance of maintaining good dental health for overall wellness.
1. Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, often resulting in chronic inflammation. Though the exact causes of these diseases remain unclear, bacterial infections are known triggers. Poor oral hygiene can lead to gingivitis and periodontal disease, creating an environment where harmful bacteria thrive and potentially contribute to autoimmune reactions.
2. Pathogen Spread
Harmful bacteria and viruses present in the mouth can enter the bloodstream, spreading to other parts of the body, including the thyroid gland. This spread may initiate or exacerbate autoimmune responses, potentially influencing thyroid function and overall health.
3. Inflammation and Thyroid Health
Chronic inflammation stemming from untreated dental infections can adversely affect the thyroid gland. Such inflammation may interfere with hormone production and regulation, leading to symptoms of thyroid dysfunction or worsening existing thyroid conditions.
4. Overall Health Connection
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is essential not only for preventing dental issues but also for promoting overall health. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups reduce the risk of infections that could compromise the immune system. For individuals with thyroid disorders, maintaining optimal oral health can help mitigate additional strain on the body.
Who Is a Biological Dentist?
A biological dentist specializes in holistic dentistry, focusing on the vital link between oral health and overall well-being. Unlike traditional dentists, biological dentists take a natural approach, using biocompatible treatments and materials that are safe for the body. Known as alternative or integrative dentistry, this field goes beyond addressing dental issues by considering how oral health impacts other systems in the body.
Individuals with specific health concerns, such as autoimmune diseases or thyroid disorders, often seek biological dentists for more personalized care. For example, patients with thyroid conditions may be concerned about toxic substances, such as mercury in dental fillings, which have been linked to thyroid dysfunction. Biological dentists address these concerns by avoiding harmful materials, such as mercury fillings or industrial fluoride, and using safer alternatives like ceramic fillings.
In addition to preventive care, biological dentists employ techniques designed to minimize toxicity and inflammation, such as ozone therapy to treat infections and promote healing. These holistic methods reduce exposure to harmful substances, supporting the immune system and promoting overall health.
By focusing on harmony between oral health and general wellness, biological dentistry offers a more natural and preventive approach to care. If you’re seeking dental treatment that prioritizes your overall health, consider consulting a biological dentist for a tailored, holistic treatment plan.
How Biological Dentists Support Thyroid and Overall Health
Biological dentists offer a holistic approach to oral care, emphasizing the connection between dental health and overall wellness, including thyroid health. For individuals with thyroid disorders or chronic conditions, this integrative approach provides significant benefits. Below are the key advantages of choosing a biological dentist:
1. Holistic Health Approach
Biological dentists recognize that oral health is deeply intertwined with the health of the entire body, including the endocrine system. They tailor treatments to reduce the risk of systemic inflammation and other complications, offering a more comprehensive approach to dental care. This is particularly beneficial for patients with thyroid disorders, as it ensures their dental treatments support, rather than hinder, their overall health.
2. Elimination of Toxic Substances
Traditional dental materials, such as mercury amalgam fillings, can release harmful toxins into the body, potentially interfering with thyroid function. Mercury is known to affect the nervous and endocrine systems, making it especially problematic for thyroid patients. Biological dentists completely avoid the use of mercury and other toxic substances, opting for biocompatible materials like composite resin. This safer alternative helps protect both oral and thyroid health.
3. Reduction of Fluoride Risks
While fluoride is commonly used in traditional dentistry, excessive exposure has been linked to thyroid dysfunction and other health concerns. Biological dentists avoid industrial fluoride and instead use natural, effective alternatives to strengthen teeth without compromising thyroid function. This approach minimizes long-term health risks while maintaining strong, healthy teeth.
4. Personalized Care with Biocompatibility Testing
Every patient’s body responds differently to dental materials, especially those with thyroid or autoimmune conditions. Biological dentists often perform biocompatibility testing to identify materials that are safest and least likely to trigger inflammatory responses. By choosing customized, body-friendly options, they reduce the likelihood of complications, making dental care more effective and comfortable for patients with specific sensitivities.
5. Preventive and Long-Term Wellness Focus
Biological dentists prioritize preventive care, emphasizing regular check-ups and non-invasive treatments to maintain oral and overall health. They take the time to understand each patient’s medical history and lifestyle, crafting individualized plans that address dental issues while supporting thyroid health. This proactive approach reduces the risk of adverse reactions, ensuring a safer and more tailored dental experience for thyroid patients.
How Do Thyroid Medications Affect Your Dental Health?
Thyroid medications can impact oral health in different ways, depending on whether you’re managing hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Here’s a closer look at how these medications interact with your dental health, as well as practical tips for maintaining good oral hygiene while undergoing thyroid treatment.
Hyperthyroidism Medications and their Effects on Dental Health
- Methimazole (Tapazole)
Methimazole is a common treatment for hyperthyroidism. It helps manage symptoms by preventing the thyroid from using iodine to produce thyroid hormones. While effective, this medication can lead to oral health issues like mouth sores, swollen salivary glands, and a bitter aftertaste. Regular mouth rinsing and maintaining good hygiene can help alleviate some of these symptoms. - Propylthiouracil (PTU)
PTU works similarly to Methimazole but also inhibits the conversion of T4 to the active T3 hormone. While it can be a lifesaver in critical hyperthyroidism cases, PTU has side effects that include mouth sores, taste changes, and an increased risk of oral infections due to its effects on vitamin K metabolism. Make sure to inform your dentist about this medication to tailor your care accordingly.
Hypothyroidism Medications and their Effects on Dental Health
- Levothyroxine (Synthroid)
For hypothyroidism, levothyroxine is commonly prescribed. It replaces the thyroid hormone that the body lacks, but long-term use can sometimes cause swelling in the lips, tongue, and throat, making swallowing and speaking difficult. Patients may also notice slower healing of oral infections, which is why routine dental visits are essential for early intervention.
Products for Oral Hygiene that Reduce Fluoride Exposure for Dental Health
Fluoride is widely recognized for its role in preventing tooth decay; however, it can also pose risks to thyroid health. Because fluoride closely resembles iodine in structure, it can bind to iodine receptors in the thyroid gland, interfering with iodine absorption. This disruption may lead to iodine deficiencies, which can contribute to conditions like hypothyroidism. As fluoride is present in many everyday products, from toothpaste to public water supplies, many individuals are now opting for fluoride-free alternatives to safeguard thyroid function and overall health.
Fluoride-Free Toothpaste Options
Several oral hygiene products are now formulated without fluoride, making them safer for those concerned about thyroid health. Some popular alternatives include:
- Coral Nano Silver Toothpaste: This innovative toothpaste is free from fluoride and contains natural ingredients, including silver nanoparticles, which provide antibacterial properties. It helps fight harmful bacteria in the mouth while offering protection against cavities and gum disease.
- Theodent Toothpaste: Theodent stands out with its unique cocoa-derived formula. It offers cavity protection without fluoride, and its proprietary compound, Rennou™, helps remineralize enamel and strengthen teeth, making it an excellent option for those looking for a fluoride-free alternative.
- Arginine-Processed Toothpaste (e.g., Colgate): Some toothpaste brands incorporate arginine, a naturally occurring amino acid to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent decay. These formulations maintain oral health effectively, while avoiding the risks associated with fluoride.
Other important practices include:
1. Brushing Your Teeth
This is a fundamental daily activity. Brushing for at least two minutes, two to three times a day, is essential for preventing tooth decay, gum disease, staining, and bad breath. It also promotes good interpersonal relationships by maintaining fresh breath.
Be sure to replace your toothbrush every three to four months, as a worn-out toothbrush is as ineffective as not brushing at all. Choosing the right toothbrush is just as important. Opt for a soft-bristled brush that fits comfortably in your mouth.
2. Flossing
Flossing is equally important for oral health. It helps protect your gums by removing food particles and debris from small gaps and tight spaces that a toothbrush cannot reach. Flossing prevents periodontal diseases, which are often caused by bacteria and plaque buildup.
However, some dental floss products contain fluoride, specifically those with PFAS (per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances) compounds. These compounds contain strong carbon-fluoride bonds and have been linked to harmful effects such as liver damage, cancer, developmental issues, and immune system impairment. Be sure to choose fluoride-free floss to avoid unnecessary exposure.
Practical Tips for Protecting Both Thyroid and Dental Health
- Maintain a rigorous oral hygiene routine, including brushing, flossing, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash.
- Inform your dentist of any thyroid conditions to ensure treatments are tailored to your needs.
- Opt for biocompatible dental materials to minimize the risk of autoimmune reactions.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups to monitor oral health and address issues early.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet to support both oral and thyroid health.
The Role of Coconut Oil in Oral Hygiene and Dental Health
Coconut oil, derived from the meat of mature coconuts, offers numerous health benefits, particularly for oral care. One popular method of utilizing coconut oil for oral hygiene is oil pulling, an ancient technique where a tablespoon of coconut oil is swished in the mouth for 15 to 20 minutes before being spit out. The oil is believed to attract and trap harmful bacteria and toxins, leaving the mouth cleaner and fresher.

Key Benefits of Coconut Oil in Oral Hygiene:
- Elimination of Harmful Bacteria:
Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which has potent antibacterial properties. It effectively eliminates harmful bacteria, such as Streptococcus mutans, a common cause of tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath. - Reduction of Plaque:
Regular oil pulling with coconut oil can help reduce plaque buildup on teeth. Plaque accumulation often leads to gum inflammation and conditions such as gingivitis. By decreasing plaque, coconut oil supports healthier gums. - Prevention of Bad Breath:
Coconut oil’s antimicrobial properties make it a natural remedy for halitosis (bad breath). Swishing the oil helps kill bacteria responsible for unpleasant odors, promoting fresher breath.
While coconut oil can significantly benefit oral hygiene, it should complement—not replace—traditional dental care practices such as brushing, flossing, eating well, and visiting the dentist regularly. Maintaining these practices is essential for optimal dental health.
Incorporating coconut oil into your oral hygiene routine, alongside a healthy diet and consistent dental care, can support a cleaner mouth and healthier gums.
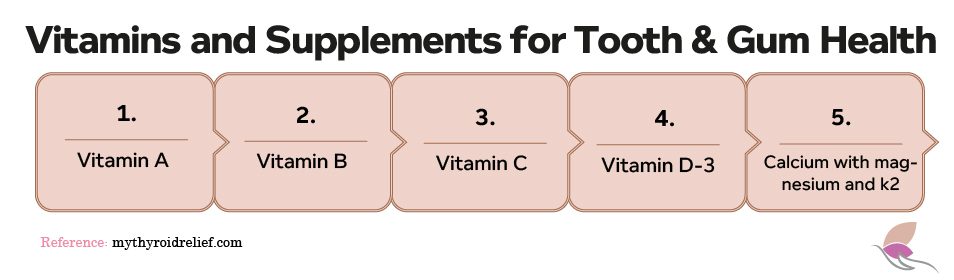
What vitamins and supplements are beneficial for tooth and gum health?
A healthy and balanced diet provides essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients needed for the growth of healthy teeth, including:
1. Vitamin A
This vitamin plays a crucial role in promoting the healing of inflamed gums and helps maintain the soft tissues of the gums. Vitamin A is also involved in the production of saliva, which acts as a natural defense against cavities and gum disease. A deficiency in vitamin A can lead to dry mouth, which increases the risk of tooth decay and oral infections.
2. Vitamin B
A deficiency in Vitamin B, especially B12, can lead to toothaches, oral sensitivity, and receding gums. Vitamin B is essential for maintaining the health of your mouth tissues and the nerve function necessary for tooth sensitivity. Additionally, it helps in the healing of damaged tissues, such as those caused by gum disease or other oral infections, making it a key nutrient for dental health.
3. Vitamin C
As a powerful antioxidant, Vitamin C is vital for gum health. It promotes healing, prevents gum inflammation (gingivitis), and supports the structural integrity of your teeth by stimulating collagen production. Collagen is a primary protein in the gums and tooth-supporting tissues, which helps prevent gum disease, tooth loss, and bleeding gums.
4. Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is essential for the proper absorption of calcium, a mineral that is crucial for strong, healthy teeth. This vitamin also helps regulate the immune system, which plays a role in preventing gum disease and inflammation. It acts as a protective agent against tooth decay, periodontal disease, and other oral health issues.
5. Calcium (with magnesium and Vitamin K2)
Calcium is the building block for strong teeth and bones. It is essential for tooth growth and development, strengthening tooth enamel, and maintaining bone density around the teeth. Magnesium works alongside calcium to ensure proper absorption and retention in bones and teeth. Vitamin K2 helps in directing calcium to the bones and teeth while preventing its deposition in soft tissues like arteries, thus supporting the integrity of the gums and the teeth’ overall health.
Conclusion
Oral hygiene involves maintaining a healthy mouth and teeth through regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups. For thyroid patients, dental care requires extra caution, as certain treatments can cause inflammation or trigger autoimmune thyroid disorders like Hashimoto’s and Graves’ disease.
Thyroid patients should consult a biological dentist to ensure compatibility of treatments and manage drug interactions. Regular dental visits (at least twice a year) are essential, along with using digital X-rays and a lead apron shield to minimize radiation exposure.
REFERENCES
Oral Hygiene: Best Practices & Instructions for Good Routine (clevelandclinic.org)
Can Dental Work, Such as Fillings, Lead to Thyroid Issues? – Thyroid Advisor
Different Types Of Dental Procedures – Miosuperhealth
Is It Possible That Your Mercury Filling Caused Your Hypothyroidism? (thyroidnation.com)
Dental Amalgams, Root Canals, And Thyroid Health | Natural Endocrine Solutions
Suffer With Thyroid Disease And Have A Scalloped Tongue (thyroidnation.com)
Macroglossia: Definition, Causes & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)
Defects of taste and smell in patients with hypothyroidism – PubMed (nih.gov)
Thyroid disorders and osteoporosis (btf-thyroid.org)
I didn’t realise that there was such a link between dental health and your thyroid. It’s so important to look after all aspects of your health.
Thanks for your comment!Yes! There is that connection and we detail it in our article! Liliana.
Hi Jenny,
You’re absolutely right; taking care of all aspects of our health is crucial. The connection between dental health and the thyroid is often overlooked, but it’s essential to recognize that our body systems are interconnected. Maintaining good dental health supports a healthy smile and can positively impact overall well-being, including the thyroid gland.
Hi Jenny!
Yes, it is surprising on how closely dental health is connected to the thyroid! It just goes to show how taking care of all aspects of our health is so important. Thanks for visiting our website.
Thank you for sharing your thoughts, Jenny! It’s surprising how interconnected our health can be, and taking care of all aspects, including dental health, is indeed crucial. If you have any more questions or topics you’d like to explore, feel free to let us know. We’re here to provide valuable insights and information to support your well-being.
I know that the dental issues can affect the heart and your cardiac system. I didn’t know that there was a connection between the dental problems and the thyroid as well.
Hi Joanna! Yes, dental health and thyroid function are interconnected. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism, and an imbalance in these hormones can cause various health problems, including oral health issues.
Thank you for your comment and for sharing your insights! You’re right that dental issues like dental work done with heavy metals can impact the heart, cardiac system, and thyroid. It’s fascinating to see how different systems in the body are interconnected. Thank you for highlighting this connection and contributing to the conversation!
HiJoanna!
Absolutely, you’re right! Dental issues can indeed have broader health implications beyond just oral health. The connection between dental problems and the thyroid may not be as widely known, but it’s an important aspect of overall health to consider. If you have any more questions feel free to ask. Thanks for reading our blog.
HiJoanna,
You’re absolutely right! Dental problems can indeed have an impact on the heart and cardiac system, and it’s important to be aware of this connection. Surprisingly, dental health can also influence thyroid health in various ways. It’s fascinating how interconnected our body’s systems can be. Thanks for reading our blog.